Accounting for foreign currency with Expensify

Wondering how to account for foreign currency in your travel expense reports? Expensify makes it simpler than ever.
What is foreign exchange accounting?
Foreign exchange accounting is the process of recording business expenses in currencies other than your own.
If you’ve ever taken a business trip to another country, for instance, then you’ve likely found yourself wondering how to get reimbursed for expenses you paid for in yen (or euros, or yuan, or any other type of foreign currency) instead of dollars.
That’s where foreign exchange accounting comes in. Sometimes referred to as FX accounting for short, foreign exchange accounting is all about accurately tracking business expenses paid for in foreign currencies.
In terms of expense reporting, foreign exchange accounting encompasses two core processes: recording expenses and calculating the exchange rate — more on those below.
Recording expenses
The first step of foreign exchange accounting is one you’re likely already familiar with — recording every business expense as it’s made in a given foreign currency.
For example, if you pay for your London hotel room in British pounds (GBP) but live and work in the U.S., you’ll need to record the expense in pounds rather than dollars.
Calculating the exchange rate
Next, either you or your accountant will use the current exchange rate to determine the cost of your expenses in your own country’s currency. (Hint: If you’re using smart spend management software like Expensify, the app will automatically take care of this step for you.)
If your hotel room cost 200 British pounds and the current exchange rate is 1.25, for instance, that expense would come out to $250 USD.
Types of foreign currency
For the purposes of travel expense reports, foreign currency can be divided into three categories: transactional, functional, and reporting.
Transactional currency is the currency in which the payment is made. Using the example above, GBP would be the transactional currency. This is the currency you’ll include on your foreign expense reports.
Functional currency is the currency your company primarily uses to conduct business. If your company is based in the U.S. and typically does business with other U.S. companies, its functional currency is USD.
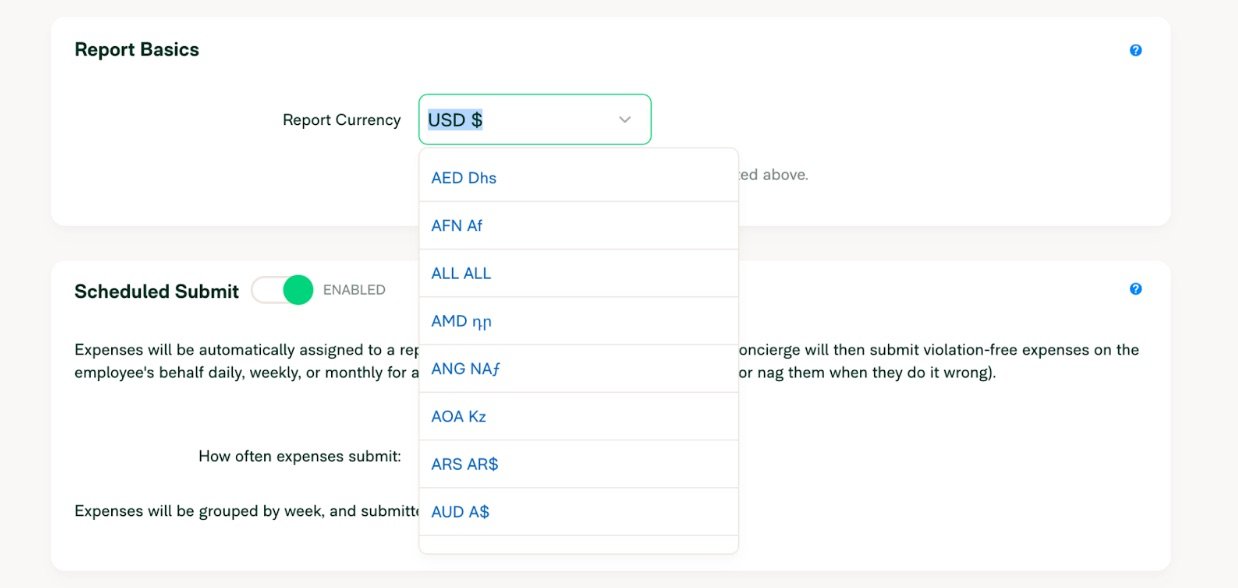
Reporting currency is the currency your company uses to create financial reports. A U.S.-based company, for example, may find it easiest to use USD as its reporting currency.
Transactions in foreign countries: what you need to know
When you’re on a business trip in a foreign country, you’ll need to track all your expenses just as you would back in your home country. So if you pay in cash, you’ll need to request a receipt. Once you have a receipt in hand, you can use SmartScan to quickly and automatically upload it to your expense report.
Want to use your company credit card instead? As long as it’s a Visa or a Mastercard, you should be good. Psst: The Expensify Card is a Visa, so we’ve got you covered in almost every country worldwide.
As a bonus, when you use the Expensify Card, your expenses are automatically imported to your expense reports — no receipt scanning required.
Track foreign currency expenses with Expensify
If you’re using manual methods to create your expense reports, you’ll be stuck looking up exchange rates and doing lots of math.
But if you’re using Expensify, your expense reporting process will get a whole lot easier. How easy are we talking? Just scan your receipts with SmartScan (or swipe your Expensify Card) and we’ll take it from there.
We convert every employee’s expenses to the same output currency, so even if you’re in Japan and your colleagues are in Australia, all your expense reports will be automatically converted to the currency your company sets.
And since Expensify can log nearly any currency in the world, you’ll be set almost anywhere you go.
Common questions about foreign expense reporting
-
In the Accounting Standards Codification (ASC), foreign currency accounting falls under Topic 830, Foreign Currency Matters. ASC 830 covers five subtopics: general guidelines, foreign currency transactions, translation of financial statements, statement of cash flows, and income taxes.
-
For many accounting teams, the biggest challenge of foreign currency transactions is staying up-to-date with exchange rates and accurately converting transactions made in multiple foreign currencies to one reporting currency.
But for companies using Expensify, that challenge is greatly reduced or even completely eliminated. We’ll translate almost any currency into a single reporting currency, so you don’t have to.
-
In many cases, the simplest solution is to put all foreign transaction gains and losses in one caption within the statement.
Or, if you need to take a more detailed approach, you can instead put each gain or loss alongside the line they’re most relevant to.
-
Traditionally, the three primary asset classes are stocks, bonds, and cash or cash equivalents. But foreign exchange doesn’t fit neatly into any of those categories, so it can be viewed as a standalone asset class of its own.
-
When we need to convert an expense from one currency to another, we use Open Exchange Rates (a trusted exchange rate database) to determine the average bid and ask price on the specific date the expense took place.
If data isn’t available for the date in question, we’ll use data from the last day the markets were open prior to the transaction taking place. So if you make a purchase on a Saturday, we’ll use data from the day before to calculate the foreign exchange rate for your expense.
And if the expense has been logged in advance, we’ll simply use the most recent data available to calculate the exchange rate.
Ditch manual expense reporting and let Expensify do the heavy lifting
Between currency exchange fees, ever-evolving exchange rates, and tedious manual expense reporting, accounting for foreign currency the old-school way can be frustrating and confusing. But with Expensify’s intuitive travel expense report service, it doesn’t have to be: We’ll handle all the calculations, data entry, and record-keeping so you can get back to business.
Convert euros into dollars in seconds with Expensify
We’ll do the legwork for you, and keep you updated on exchange rates.
Expensify values your privacy. We’ll never sell your personal information to others.